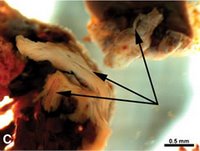
 Under normal circumstances, paleontologists take great care in unearthing the fossilized dinosaur bones without inflicting any damage. In this case however, they were forced to break the bone in two so as to fit it into the transport helicopter. To the surprise of scientists, this act revealed stretchy and flexible soft tissue which includes blood vessels, bone cells and perhaps even blood cells.
Under normal circumstances, paleontologists take great care in unearthing the fossilized dinosaur bones without inflicting any damage. In this case however, they were forced to break the bone in two so as to fit it into the transport helicopter. To the surprise of scientists, this act revealed stretchy and flexible soft tissue which includes blood vessels, bone cells and perhaps even blood cells. A scanning electron microscope revealed that the dinosaur blood vessels, which are 70 million years old, are virtually identical to those recovered from modern ostrich bones. The ostrich is today’s largest bird, and many paleontologists believe that birds are the living descendants of dinosaurs. Scientists may be able to confirm this evolutionary relationship if they can isolate certain proteins from the recently discovered T. rex tissue. These proteins could also help solve another puzzle: whether dinosaurs were cold-blooded like other reptiles or warm-blooded like mammals.
Does this discovery of soft dinosaur tissue mean that scientists will soon be able to clone a Tyrannosaurus rex? Probably not – most scientists believe that DNA cannot survive for 70 million years. Then again, before this discovery, most scientists believed that soft tissue could not survive for 70 million years either.
Link & Image: Science Now via Slashdot
Tags: Soft Tissue | Dinosaur | Bone | DNA | Nature
Comments